Artificial intelligence is often associated with advanced research or large enterprises, but its most valuable impact comes from practical, everyday business applications. Many organizations already use AI in routine processes without recognizing it as AI-driven technology.
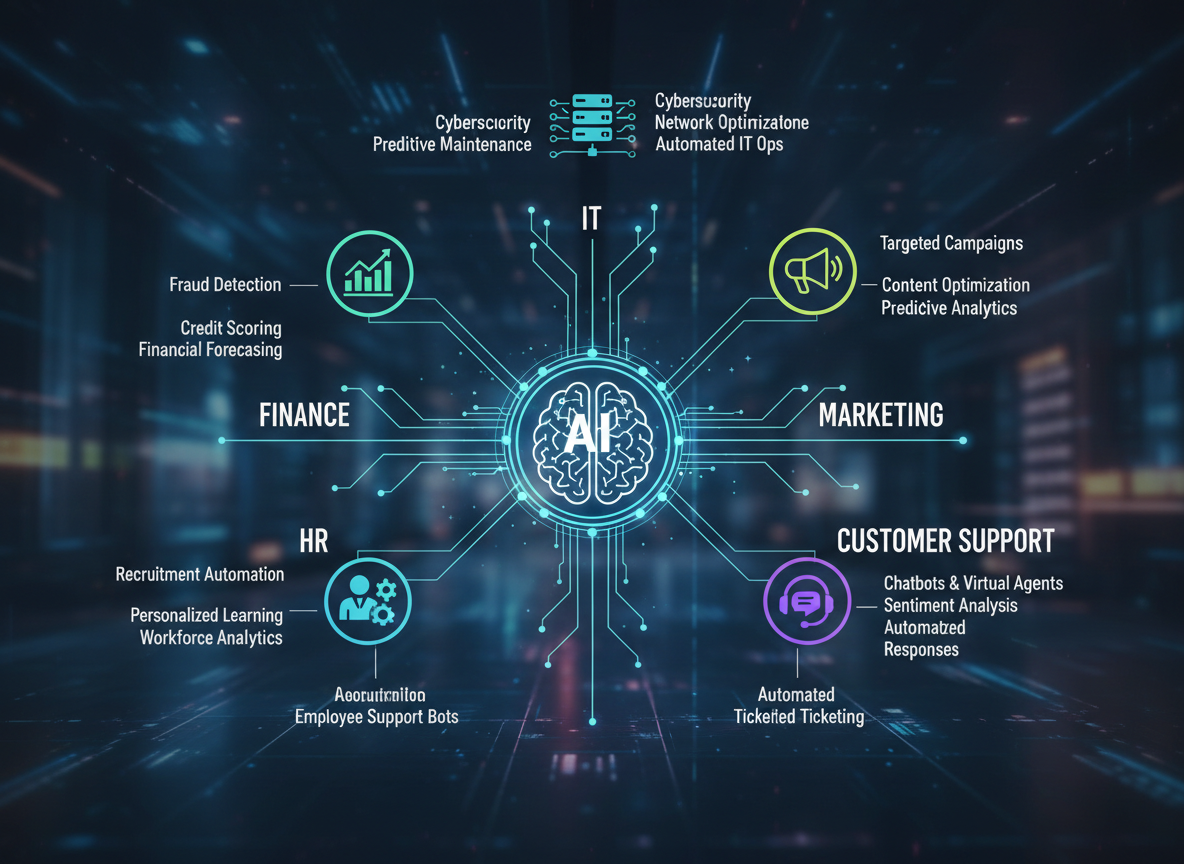
In finance operations, AI is commonly used for invoice processing, expense categorization, and fraud detection. AI systems automatically extract data from documents, validate entries, and flag anomalies, reducing errors and processing time.
In HR, AI supports resume screening, employee engagement analysis, and workforce planning. These systems analyze patterns across hiring and performance data to support more informed HR decisions.
Marketing teams rely on AI for campaign optimization, audience segmentation, and content recommendations. AI analyzes engagement behavior to improve targeting accuracy and reduce wasted spend.
IT teams use AI for system monitoring and incident detection. AI-powered monitoring tools identify unusual patterns in system behavior, enabling faster resolution and minimizing downtime.
Customer support operations also benefit significantly. AI chatbots handle repetitive queries, while sentiment analysis tools help prioritize customer issues based on urgency and tone.
Across these use cases, the key benefit is consistency. AI executes tasks reliably at scale, reducing dependency on manual effort and improving overall process stability.
The most successful AI implementations focus on specific, well-defined problems. Rather than attempting broad transformation, businesses achieve better results by embedding AI into existing workflows incrementally.
AI’s value lies in its practicality. When applied to everyday processes, it delivers measurable efficiency gains without disrupting operations.













Leave a comment